News
America’s Top 15 Earners and What They Reveal About the U.S. Tax System
Published
2 years agoon
by ProPublica
ProPublica is a Pulitzer Prize-winning investigative newsroom. Sign up for The Big Story newsletter to receive stories like this one in your inbox.Series: The Secret IRS Files Inside the Tax Records of the .001%
Periodically, we get a glimpse into the financial lives of the ultrarich. A pro athlete signs a huge contract, a tech CEO sells a boatload of shares in their company, or a billionaire heir unloads a Manhattan penthouse. Based on these nuggets of information, the media speculates as to how much income the rich might bring in every year. But nobody actually knows.
Thanks to an analysis of its unprecedented trove of IRS data, ProPublica is revealing the 15 people who reported the most U.S. income on their taxes from 2013 to 2018, along with data for the rest of the top 400.
The analysis also shows how much they paid in federal income taxes — and it demonstrates how the American tax system, which theoretically makes the highest earners pay the highest income tax rates, fails to do so for the people at the very top of the income pyramid.
The top 400 earners pay noticeably lower tax rates than the merely rich; and, if you include payroll taxes, a married couple making $200,000 a year could end up paying higher tax rates than a person making $200 million a year. (The full analysis is here; it includes selected names beyond the top 15.)
Names That Won’t Surprise You
Scan the names on the list of the top 15 income earners and you’re certain to recognize several names — or at least the names of the companies they founded. Bill Gates hasn’t been involved in the day-to-day operations of Microsoft for over a decade, yet he still earned the most during the years we studied, reporting an average yearly income of $2.85 billion — and an effective federal income tax rate of 18.4%. Steve Ballmer, his former colleague, is also a well-known public figure, both for his time as Microsoft CEO and his current ownership of the Los Angeles Clippers NBA team.
Ballmer’s average annual reported income of $1.05 billion landed him in the 10th spot on the list, and his effective federal income tax rate was 14.1%. The other side of the PC/Mac wars is represented here by Laurene Powell Jobs, widow of Apple founder Steve Jobs.
Her average reported income of $1.57 billion ranked fifth-highest; she paid an effective tax rate of 14.8%. (ProPublica sought comment from everyone mentioned in this article. Nobody disputed the numbers cited here. Unless otherwise noted, representatives for people named in this article either declined to comment, declined to comment on the record or did not respond to requests for comment.)
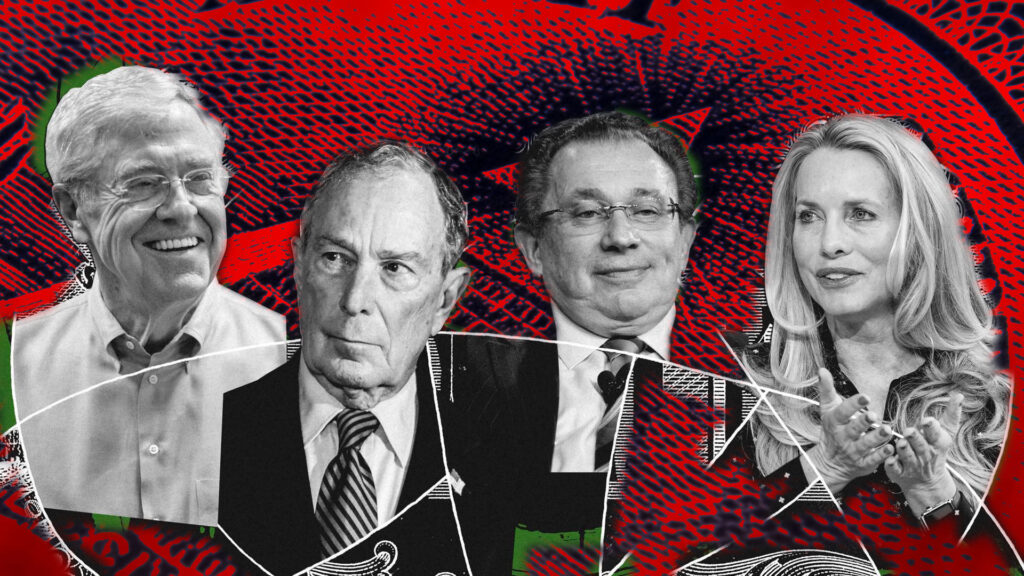
Another well-known billionaire sits just below Gates on the list: Media and tech mogul and former New York City mayor Michael Bloomberg, with an average reported income of just over $2 billion, paid an effective income tax rate of 4.1%, by far the lowest rate among the top 15. (A spokesperson told ProPublica for an earlier article that Bloomberg “pays the maximum tax rate on all federal, state, local and international taxable income as prescribed by law,” and cited Bloomberg’s philanthropic giving.)
The presence of Amazon founder Jeff Bezos — either the first- or second-wealthiest person in America, depending on the day — won’t shock most people, but Bezos’s annual reported income during these years of $832 million put him only at number 15. He paid an effective tax rate of 23.2%; as we’ve previously reported, Bezos had so little income in a couple of recent years that he was able to pay $0 in federal income taxes in those periods.
Who Are These Others and Why Are They Paying Higher Tax Rates?
Tech billionaires dominate the top 15, but hedge fund managers account for a full third of the names on this list, and some of their incomes were just as huge. Most of them paid relatively high effective tax rates, especially compared to most of the tech sector representatives. Hedge fund managers often make their money through short-term trades, which are taxed at a much higher rate than when tech titans cash in on long-term investments.
The highest-earning hedge funder is Ken Griffin, founder of the Chicago-based firm Citadel. From 2013 to 2018, he reported an average income of nearly $1.7 billion, putting him fourth on the list. Griffin paid a tax rate of 29.2% during these years. (A spokesperson for Griffin said the tax rates in the IRS data “significantly understate” what Griffin pays, because they were lowered by charitable contributions and do not reflect local and state taxes. He also said Griffin pays foreign taxes, which aren’t included in IRS calculations of effective tax rate.)
Israel Englander, co-founder of Millennium Management, paid at a 30.8% rate, while the co-founders of Two Sigma Investments, David Siegel and John Overdeck, paid tax rates of 31.6% and 34.2%, respectively.
Some of this variation in rates reflects how people structure their businesses under tax law. Income earned by publicly traded corporations is taxed at the company level. When it’s passed on to big shareholders, such as tech billionaires, it can come in the form of dividends, which are taxed at lower rates than ordinary income. By contrast, the income from some manufacturing companies and hedge funds flows directly to company owners, who pay taxes on it, resulting in higher effective tax rates on average.
Where Are the Heirs?
Lists of the world’s wealthiest individuals are always heavily populated by heirs, ranging from descendents of old money to scions of more recently minted fortunes. Dozens of heirs made ProPublica’s list of 400 biggest income earners. Descendents and relatives of Sam Walton, founder of Walmart, claim 11 spots.
The DeVos family, heirs to the Amway fortune, also have multiple members in the top 400. Perhaps the best known is Betsy DeVos, who served as U.S. secretary of education during the Donald Trump administration. With a reported annual income of $112 million, she was the 389th-highest earner in this period.
Much like the tech titans who top the list, most of these heirs get their income from dividends or long-term investments, which are taxed at a lower rate. Their effective tax rates ranged from as low as 10.6% for Betsy DeVos to a high of 23% paid by Walmart heirTom Walton.
Don’t Forget the Deductions
Another key way that some top earners reduced their tax liability was to claim significant deductions, often in the form of large charitable contributions. This is particularly true for wealthy investors who are able to make their donations with shares of stock. Thanks to a generous provision of the tax code, they can then deduct the full value of the stock at its current price — without having to first sell it and pay capital gains tax.
Michael Bloomberg achieved a tax rate of 4.1% from 2013 to 2018 by taking annual deductions of more than $1 billion, mostly through charitable contributions. From 2013 to 2017, he also wrote off an average of $400 million each year from what he’d paid in state and local taxes. The 2018 tax overhaul limited that deduction to $10,000 — but also introduced a huge new deduction for pass-through companies that Bloomberg benefited from.
Wait — What About the Celebrities?
The earnings of actors, musicians and sports stars are a subject of nonstop scrutiny in the media, yet few celebrities cracked the list of the top 400 earners, which would have required them to report annual incomes of at least $110 million.
ProPublica’s trove has data on many celebrities. One who came close to the top 400 is basketball superstar LeBron James, who averaged $96 million a year in reported income. Grammy-winning singer Taylor Swift also came within reach of the top 400, averaging $82 million in reported income during these years. Actor George Clooney would have had to double his average income of $55 million to crack the top 400.
THE TOP 15
Here are the details on the top 15 income earners. Read the full analysis of the top 400 here.
For the full list of America’s top 400 income earners and their tax rates, along with our methodology, click here.
Newest stories:
- What if “Non-human Biologics” are Watching?
- ‘Most Significant Charges Yet’: Trump Indicted for Trying to Overturn 2020 Election
- But what am I?’ Pee-wee Herman creator and star, Paul Reubens dead at 70
- The Congressional Hearing On UFOs Confirmed the Existence of Aliens? Maybe
- The Earthly Frontier: Building a Sustainable Future at Home
Find books on Music, Movies & Entertainment and many other topics at Bookshop.org
Lynxotic may receive a small commission based on any purchases made by following links from this page