Drought that looked invincible has met extreme opposite weather: stalemate?
Atmospheric river storms can actually be welcome in California during a historic drought, like the one this year. In some cases, nearly 50% of California’s precipitation each year can be the result of atmospheric rivers, and they can bring enough water to stop even a historic drought in its tracks.
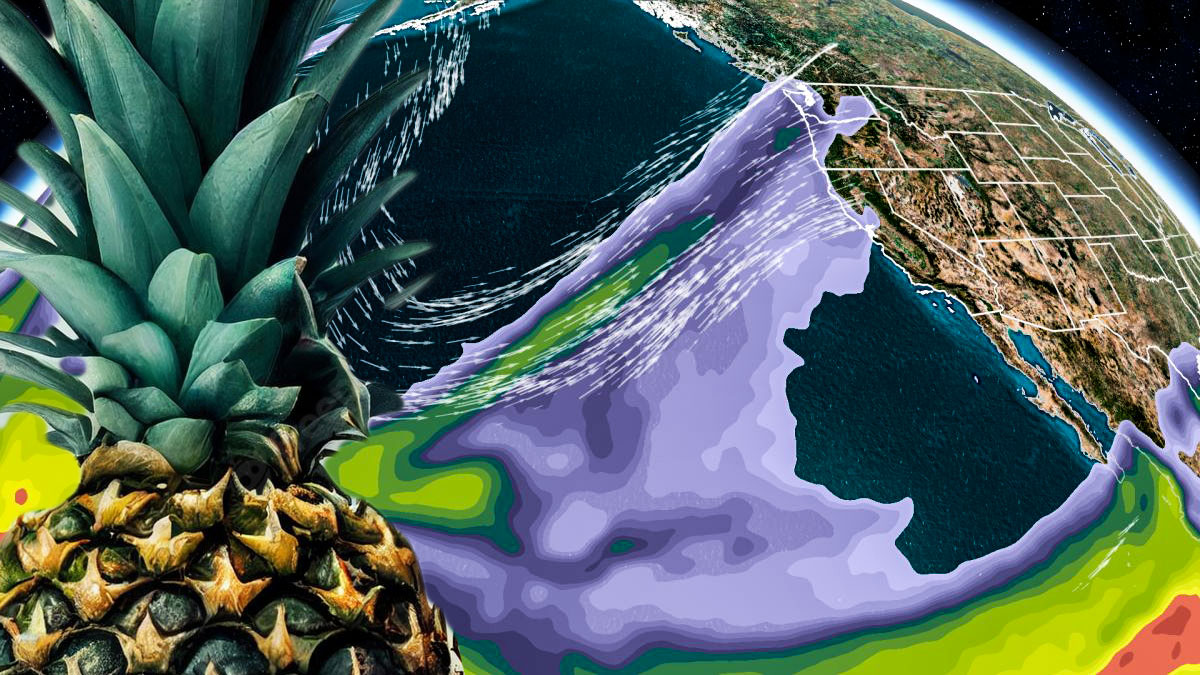
Atmospheric river storms, also known as “pineapple express” storms, have sometimes been known to bring much-needed rain and snow to drought-stricken areas, including California.
Extreme weather, wildfires, and more have been on the increase worldwide as a result of global warming and climate change.
Atmospheric river storms are characterized by a narrow corridor of strong winds and heavy precipitation that can extend for thousands of miles. They are often associated with the transport of moist air from tropical regions, and they can be a significant source of water for many areas.
In California, atmospheric river storms can provide a much-needed source of water for agriculture, hydroelectric power generation, and other important water-dependent activities.
They can also help to replenish reservoirs and groundwater aquifers, which can help to mitigate the impacts of drought.
The monumental drought of 2022 in the rearview?
Just as it was looking as if there was zero chance for enough moisture to reverse the long, intense drought conditions that California has suffered this year, the “Pineapple Express” became a holiday storm front. There is a sense of relief, although it is too early to tell if the drought will end as a result of this rain.
It is also important to note that these storms can also bring heavy rainfall and strong winds, which can lead to flooding and other hazards. As a result, it is important for people in affected areas to be prepared and take necessary precautions.
An atmospheric river is a narrow band of moisture-rich air that extends from the tropics or subtropics to higher latitudes. These rivers of air are typically about a thousand miles wide and several thousand miles long, and they can transport enormous amounts of water vapor from the tropics to other parts of the world.
Atmospheric rivers are important because they play a crucial role in the global water cycle.
Water evaporates from the surface of the ocean, rises into the atmosphere, and then condenses to form clouds. As the clouds move over land, they release their moisture in the form of rain or snow.
Atmospheric rivers are responsible for a large portion of the moisture that falls as precipitation in many parts of the world, particularly along the western coasts of the United States, Europe, and Asia.
Atmospheric rivers can be either warm or cold, depending on the temperature of the air that they are carrying.
Warm atmospheric rivers are typically associated with heavy rainfall and floods, while cold atmospheric rivers can bring snow and ice to colder regions.
One of the most well-known atmospheric rivers is the “Pineapple Express,” which is a warm atmospheric river that brings moist air from the tropics to the Pacific Northwest of the United States.
The Pineapple Express is named after the tropical fruit because it brings warm, tropical air to the region. This atmospheric river is responsible for a large portion of the precipitation that falls in the Pacific Northwest, and it can cause heavy rainfall and floods in the region.
Another well-known atmospheric river is the “North Atlantic Oscillation,” which is a cold atmospheric river that brings moist air from the subtropics to the northeastern United States and eastern Canada.
This atmospheric river is responsible for a large portion of the snowfall that falls in these regions, and it can cause heavy snow and ice storms.
Atmospheric rivers can have a significant impact on the weather and climate of the regions that they affect.
They can bring much-needed moisture to dry regions, which can help to alleviate drought conditions. However, they can also cause heavy rainfall and floods, which can lead to damage to infrastructure and loss of life.
In recent years, there has been an increasing awareness of the importance of atmospheric rivers and their potential impact on the global water cycle.
Scientists are working to better understand atmospheric rivers and to develop better tools for predicting and managing their effects.
This research is important because atmospheric rivers are likely to become more intense and more frequent in the future due to climate change.
Generally speaking, an atmospheric river is a narrow band of moisture-rich air that extends from the tropics or subtropics to higher latitudes.
These rivers of air play a crucial role in the global water cycle and can bring much-needed moisture to dry regions or cause heavy rainfall and floods.
There is an increasing awareness of the importance of atmospheric rivers and their potential impact on the global water cycle, and scientists are working to better understand and predict their effects.
Please help keep us publishing the content you love
- What if “Non-human Biologics” are Watching?
- ‘Most Significant Charges Yet’: Trump Indicted for Trying to Overturn 2020 Election
- But what am I?’ Pee-wee Herman creator and star, Paul Reubens dead at 70
- The Congressional Hearing On UFOs Confirmed the Existence of Aliens? Maybe
- The Earthly Frontier: Building a Sustainable Future at Home
Lynxotic may receive a small commission based on any purchases made by following links from this page